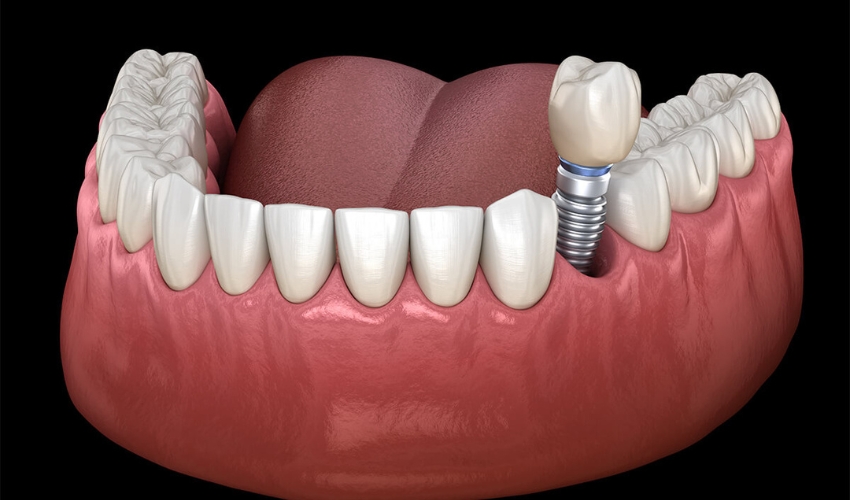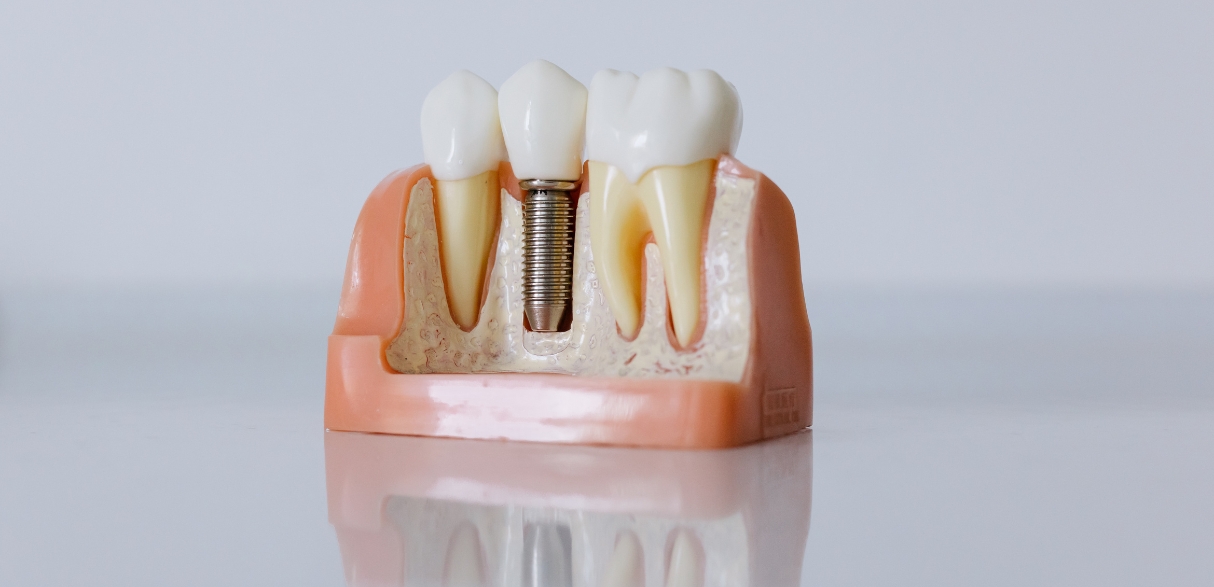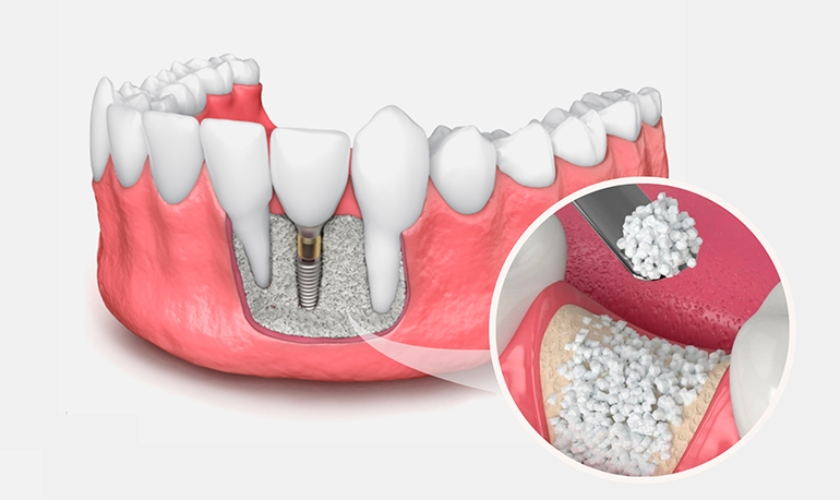
A bone graft for dental implants involves transferring natural or synthetic tissue, or a combination of both, to your jawbone to restore areas with low bone volume or density. When teeth are missing, the jawbone can shrink because tooth roots normally stimulate and maintain bone mass. Therefore, bone grafting is often necessary for those seeking dental implants but lacking sufficient healthy bone. The American Academy of Implant Dentistry notes that bone levels can decrease by 25 percent within the first three months after tooth loss and by up to 50 percent within the first six months.
What is a Bone Graft?
A bone graft involves placing material into the jawbone to promote new bone growth and create a more stable base for dental implants. The goal is to provide sufficient bone density and volume to support the implant and ensure long-term success.
What Are the Types of Bone Grafts Used for Dental Implant Placement?
There are four primary types of bone grafts used in dental implant placement:
- Socket preservation
- Ridge Augmentation
- Sinus lift
- Nerve repositioning
The American Academy of Osseointegration highlights that certain conditions related to dental implants might necessitate additional procedures, such as bone grafts, either before, during, or after implant placement, to ensure their long-term success.
Oral surgeons are experienced in performing these jawbone grafting procedures. Before recommending a bone graft, your surgeon will conduct a 3-D cone beam CT scan to evaluate the quality and volume of your bone. Understanding the different types of grafting procedures and their functions can help you feel more at ease with your treatment.
1. Socket Preservation
Socket preservation is a bone grafting technique aimed at maintaining and reconstructing the socket—the bone that supports a tooth—after a tooth is lost or extracted. When a tooth is missing, the empty socket can lead to bone shrinkage or collapse since there is no longer any stimulation to the bone from the tooth. Ensuring a healthy socket is crucial for the success of future dental implants.
Socket Preservation Procedure
Typically performed by oral surgeons following tooth extraction, socket preservation involves these steps:
- A thin sheet of material is placed between the gum and bone to prevent gum cells from interfering with the growth of bone cells.
- Filling the socket with either natural or synthetic bone material.
- Covering the area with tissue or an artificial membrane to support bone growth and repair.
This procedure helps preserve the bone’s height and width, preventing future bone loss and avoiding more complex and costly surgeries later on.
Healing Time
You should expect a healing period of three to six months following socket preservation.
2. Ridge Augmentation
Ridge augmentation is a bone grafting technique aimed at increasing the width and volume of the alveolar bone, which supports the teeth and forms their sockets. Bone ridge loss can occur due to missing teeth, jaw deformities, disease, or trauma. Unlike socket preservation, which is done immediately after tooth extraction, ridge augmentation is performed when bone loss has already happened. This procedure helps restore the jaw’s shape and provides a solid foundation for dental implants.
Ridge Augmentation Procedure
The ridge augmentation procedure involves the following steps:
- Lifting the gum tissue to reveal areas where bone is missing.
- Filling the area with bone or a bone substitute that acts as a scaffold for new bone growth.
- Suturing the gum tissue over the area and allowing your body to regenerate the lost bone and tissue.
Your oral surgeon will discuss the best graft materials to ensure adequate bone quality for your dental implants.
Healing Time
Ridge augmentation typically requires about six months to heal.
3. Sinus Lift
A sinus lift, also known as sinus augmentation, is a bone grafting procedure designed to elevate the sinus floor in the upper rear jaw and introduce new bone material. When upper back teeth are missing, the sinuses may encroach into the space previously occupied by tooth roots. Without a sinus lift, dental implants could penetrate the sinus membrane, compromising their placement.
Sinus Lift Procedure
The sinus lift procedure generally involves the following steps:
- Making an incision in the gum to expose the underlying bone.
- Creating a small opening in the bone and gently lifting it into the sinus cavity.
- Filling the resulting space with bone graft material.
- Closing the incision and allowing time for the bone to grow and integrate.
A sinus lift can enhance the results of individual implants or implant-supported dentures.
Healing Time
Following a sinus lift, you will usually need to wait four to six months before receiving a dental implant.
4. Nerve Repositioning
In some cases, repositioning the nerve that runs through the lower jaw may be necessary to accommodate dental implants. This procedure is typically considered only after other, less invasive options have been explored. Nerve repositioning creates space for implants and bone graft material by moving the nerve, but it requires a high level of expertise to avoid nerve damage. Potential risks include temporary or permanent numbness in the lower lip or jaw.
Nerve Repositioning Procedure
The procedure usually involves:
- Removing a section of the outer lower jawbone to access the nerve and blood vessel canal.
- Carefully isolating and repositioning the nerve and vessel bundle.
- Placing the dental implant.
- Releasing the nerve and vessel bundle back into position.
- Adding bone graft material.
- Closing the surgical site.
Nerve repositioning may be necessary if you have experienced significant lower tooth and jawbone loss and need dental implants.
Healing Time
The recovery period for nerve repositioning and implant placement is typically about six months.
Bone Grafting Benefits
Beyond providing a stable foundation for dental implants, bone grafting offers several additional advantages, according to the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons:
- Enhanced chewing ability
- Improved aesthetic results
- Better function and speech
Bone grafting is a vital step in the dental implant process for many patients, providing the necessary support for successful implantation. Understanding the different types of bone grafts—socket preservation, ridge augmentation, sinus lift, and nerve repositioning—can help patients make informed decisions and work with their dental professionals to achieve the best outcomes. Discussing your options with your dentist or oral surgeon will ensure that the selected graft type aligns with your specific needs and goals, leading to a successful and effective dental implant experience.